A movie that understands the principle of transistors that are indispensable for modern civilization such as computers and smartphones
A transistor is an element that amplifies electrical signals and controls the on/off of currents by electrical signals. Transistors are necessary parts for assembling
How Transistors Work-YouTube
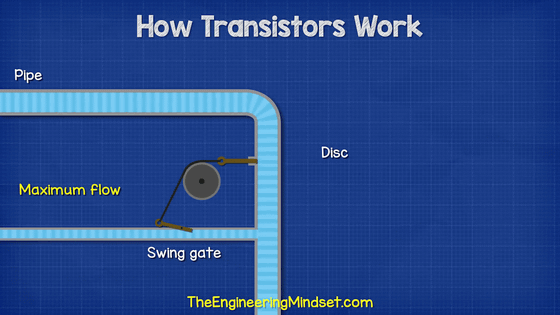
Transistors are often described in terms of water supply. The base current that flows through the transistor is the water that flows through the pipe. The water flow in this pipe is blocked by a plug (Disc). And the stopper is linked with the 'Swing gate' in the thin tube flowing next to the pipe.
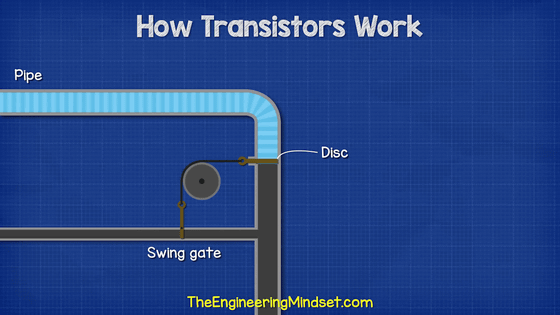
When a small amount of water flows through the thin pipe, the swing gate opens, and the pipe stopper opens in conjunction. In other words, if water flows through a thin tube, the water in the pipe also flows, and the base current controls the current flowing in another part.
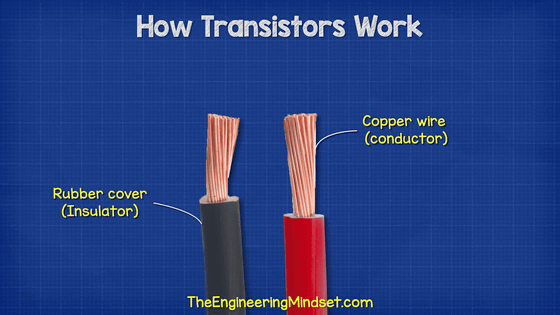
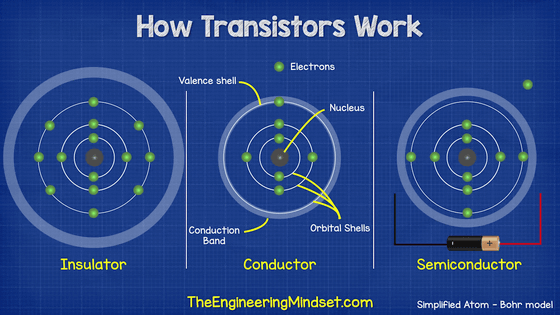
Of course, water does not flow in the actual transistor. Materials used in transistors are called semiconductors. Materials that easily conduct electricity are called 'conductors', and those that do not conduct electricity easily are called 'insulators'. Semiconductors are in the middle.
To understand what a semiconductor is, we need to understand the structure of atoms. Below is a simple
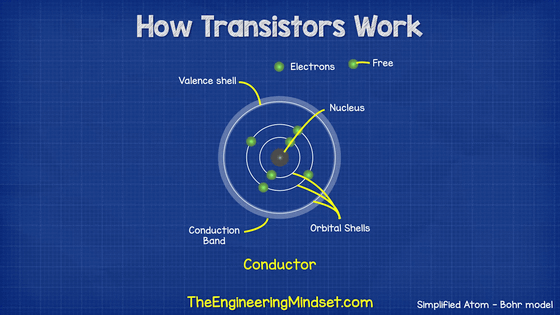
The conduction band is the energy band outside the outermost shell, and electrons excited in this conduction band can behave relatively freely. Insulators have the property that it is difficult for electricity to flow because the electrons in the outermost shell are difficult to excite into the conduction band. Conversely, in conductors such as metals, the electrons in the outermost shell are easily excited to the conduction band, so electricity flows easily. And semiconductors have the property that the ease of conducting electricity changes when heat or electricity is applied.
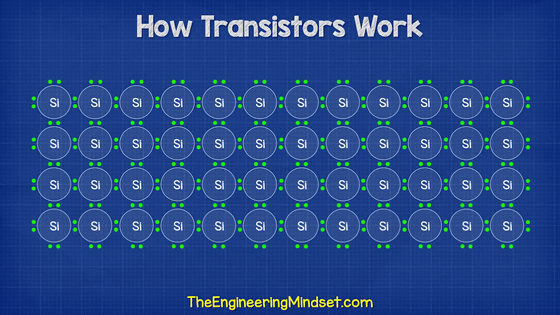
The semiconductors used in transistors are '
The four electrons in the outermost shell of silicon (Si) are 'valence electrons' used in reactions with other atoms, so to speak, one atom has four hands. Then, four silicon atoms are bonded to one silicon atom by a '
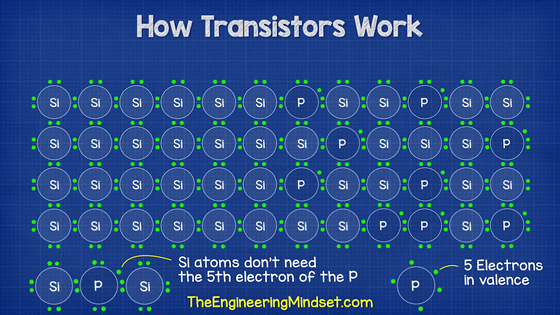
Then, the N-type semiconductor is to inject phosphorus (P) into this silicon structure in a process called doping. Phosphorus has five valence electrons, so if it is incorporated into the structure of silicon, which has four valence electrons, it will inevitably have surplus electrons.
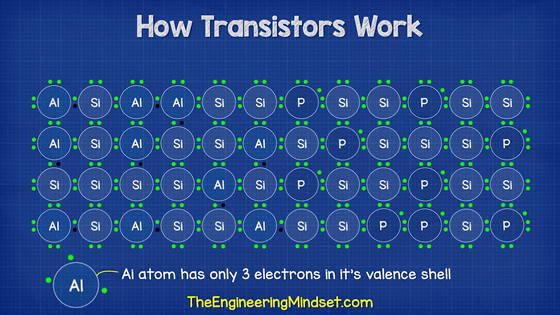
Conversely, P-type semiconductors are those in which atoms with only three valence electrons, such as aluminum (Al) and boron, are implanted into the silicon structure. Contrary to N-type semiconductors, P-type semiconductors inevitably run out of electrons.
When this N-type semiconductor and P-type semiconductor are joined, electrons are exchanged on the contact surfaces. However, the electrons only move on the contact surface, and the electrons do not move throughout the semiconductor.
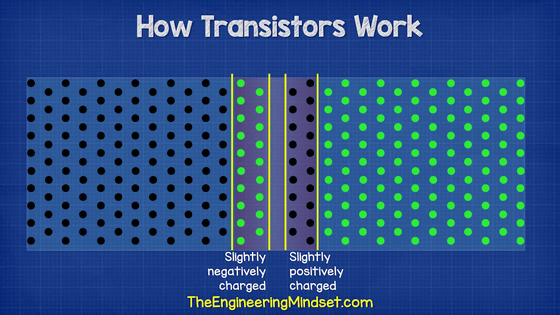
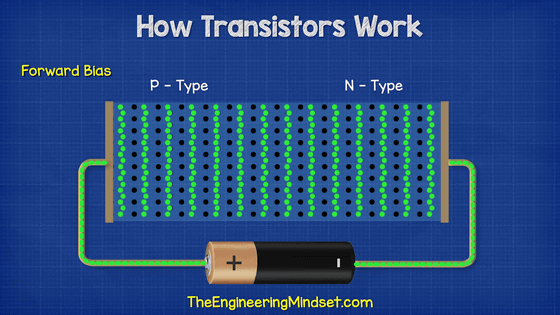
However, when a voltage above a certain level is applied to these two semiconductors, electrons move.
A transistor has a structure that combines this N-type semiconductor and P-type semiconductor, and there are two types: NPN type and PNP type.
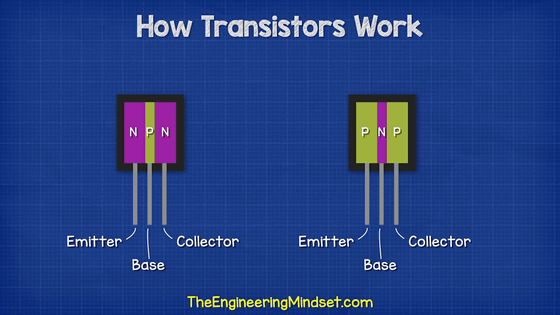
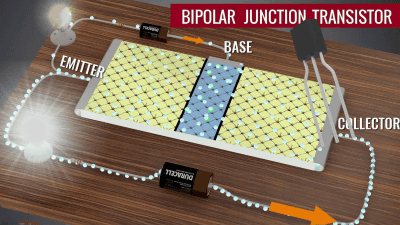
A transistor has three poles: emitter, base, and collector. In the case of the NPN type, the emitter is connected to one N-type semiconductor, the base is connected to the central P-type semiconductor, and the collector is connected to the other N-type semiconductor.
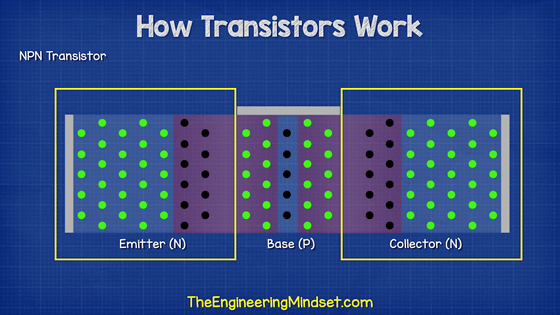
When a small current is passed through the emitter and base, electrons begin to move between the N-type and P-type semiconductors on the emitter side.
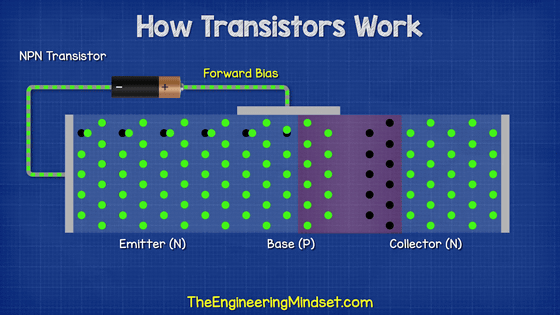
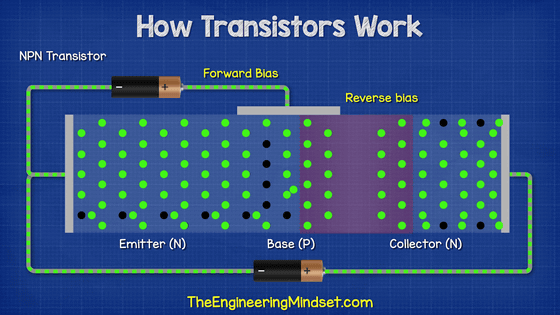
A current flows when the emitter and collector are connected. By passing a small amount of current through the emitter and base, a large current change is created between the emitter and collector, allowing the transistor to amplify the input signal and switch the current on and off. Since this 'current on / off' can express binary numbers 0 and 1, the transistor becomes an important part for configuring the logic circuit of the computer.
Related Posts: