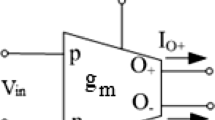
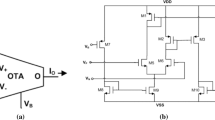
Abstract
This paper presents grounded and floating memristor emulators based on current differencing transconductance amplifier. These emulators are realized using current differencing transconductance amplifier, operational transconductance amplifier and a grounded capacitor. Incremental to decremental memristor emulators and vice versa are easily obtained by modifying the circuit slightly. These memristor emulators are very simple in design over other complex realizations reported in the literature. The pinched hysteresis curves have been obtained without using analog multiplier for a wide range of frequency that varies from 600 kHz to 2 MHz. The property of retention has been verified for proposed design of memristor emulators after applying voltage pulse of amplitude 100 mV and frequency 1 MHz. Non-ideal analysis including the effects of parasitic impedances on the behaviour of proposed memristor emulators has also been presented. The proposed designs of memristor emulators have been simulated by Mentor Graphics Eldo simulation tool with TSMC 0.18 µm, level 53, CMOS technology parameters. The performance of proposed memristor emulator is verified by embedding it in the realization of current- mode analog filter.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, L. (1971). Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory,18(5), 507–519.
Strukov, D. B., Snider, G. S., Stewart, D. R., & Williams, R. S. (2008). The missing memristor found. Nature Publishing Group,453(7191), 80.
Lopez, S. C., Lopez, M. J., Aguilar, M. A. C., & Lopez, F. E. M. (2013). A simple floating memristor emulator circuit based on current conveyors. IEEE 10th international conference on electrical engineering, computing science and automatic control (CCE) (pp. 445–448).
Yu, D., Ching Iu, H. H., Fitch, A. L., & Liang, Y. (2014). A floating memristor emulator based relaxation oscillator. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers,61(10), 2888–2896.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2014). A new DDCC based memristor emulator circuit and its applications. Microelectronics Journal,45(3), 282–287.
Kumngern, M. (2015). A floating memristor emulator circuit using operational transconductance amplifiers. In IEEE international conference on electron devices and solid-state circuits (EDSSC) (pp. 679–682).
Alharbi, A. G., Khalifa, Z. J., Fouda, M. E., & Chowdhury, M. H. (2015). A new simple emulator circuit for current controlled memristor. In: IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits, and systems (ICECS) (pp. 288–291).
Abuelma’atti., M. T., & Khalifa, Z. J. (2015). A continuous-level memristor emulator and its application in a multivibrator circuit. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,69(4), 771–775.
Lopez, S. C., Aguilar, M. A. C., & Muniz-Montero, C. (2015). A 16 Hz–160 kHz memristor emulator circuit. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,69(9), 1208–1219.
Kumngern, M., & Moungnoul, P. (2015). A memristor emulator circuit based on operational transconductance amplifiers. In IEEE 12th international conference on electrical engineering/electronics, computer, telecommunications and information technology (ECTI-CON) (pp. 1–5).
Alharbi, A. G., Fouda, M. E., & Chowdhury, M. H. (2015). A novel memristor emulator based only on an exponential amplifier and CCII+. In IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits, and systems (ICECS) (pp. 376–379).
Abuelma’atti, M. T., & Khalifa, Z. J. (2016). A new floating memristor emulator and its application in frequency-to-voltage conversion. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing,86(1), 141–147.
Sozen, H., & Cam, U. (2016). Electronically tunable memristor emulator circuit. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing,89(3), 655–663.
Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2017). Floating memristor emulator with subthreshold region. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing,90(2), 471–475.
Rashad, S. H., Hamed, E. M., Fouda, M. E., AbdelAty, A. E., Said, L. A., & Radwan, A. G. (2017). On the analysis of current-controlled fractional-order memristor emulator. In IEEE 6th international conference on modern circuits and systems technologies (MOCAST) (pp. 1–4).
Ranjan, R. K., Rani, N., Pal, R., Paul, S. K., & Kanyal, G. (2017). Single CCTA based high frequency floating and grounded type of incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. Microelectronics Journal,60, 119–128.
Ranjan, R. K., Raj, N., Bhuwal, N., & Khateb, F. (2017). Single DVCCTA based high frequency incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,82, 177–190.
Ayten, U. E., Minaei, S., & Sagbas, M. (2017). Memristor emulator circuits using single CBTA. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,82, 109–118.
Babacan, Y., Yesil, A., & Kacar, F. (2017). Memristor emulator with tunable characteristic and its experimental results. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,81, 99–104.
Cam, Z. G., & Sedef, H. (2017). A new floating memristance simulator circuit based on second generation current conveyor. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers,26(02), 1750029.
Petrovic, P. B. (2018). Floating incremental/decremental flux-controlled memristor emulator circuit based on single VDTA. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing,96(3), 417–433.
Yesil, A. (2019). Floating memristor employing single MO-OTA with hard-switching behavior. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers,28(02), 1950026. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126619500269.
Yesil, A. (2018). A new grounded memristor emulator based on MOSFET-C. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,91, 143–149.
Ranjan, R. K., Sharma, P. K., Sagar., Raj, N., Kumari, B., & Khateb, F. (2018). Memristor emulator circuit using multiple-output OTA and its experimental results. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218126619501664.
Kanyal, G., Kumar, P., Paul, S. K., & Kumar, A. (2018). OTA based high frequency tunable resistorless grounded and floating memristor emulators. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,92, 124–145.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2019). Electronically tunable memristor based on VDCC. AEU -International Journal of Electronics and Communications,107, 282–290.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2019). Design and experimental evolution of memristor with only one VDTA and one capacitor. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems,38(6), 1123–1132.
Vista, J., & Ranjan, A. (2019). A simple floating MOS-memristor for high-frequency applications. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration VLSI Systems,27(5), 1186–1195.
Hassanein, A. M., Elsafty, A. H., Said, L. A., Madian, A. H., & Radwan, A. G. (2018). Incremental grounded voltage controlled memristor emulator. In 2018 30th international conference on microelectronics (ICM) (pp. 156–159).
Xie, X., Zou, L., Wen, S., Zeng, Z., & Huang, T. (2019). A flux-controlled logarithmic memristor model and emulator. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing,38(4), 1452–1465.
Yadav, N., Rai, S. K., & Pandey, R. (2020). New grounded and floating memristor emulators using OTA and CDBA. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1002/cta.2774.
Uygur, A., & Kuntman H. (2005). Design of a Current differencing transconductance amplifier (CDTA) and its application on active filters. In 13th IEEE conference on signal processing and communication applications (pp. 340–343).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Rai, S.K. New Grounded and Floating Decremental/Incremental Memristor Emulators Based on CDTA and Its Application. Wireless Pers Commun 113, 773–798 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07252-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07252-y