

Silt, is a solid sediment that is similar to dust. It can be transported and deposited by water, ice and wind.
Silt is made up of particles of rock and mineral particles that are larger than clay but smaller than sand.
To be classified as silt, a particle needs to be smaller than .005cm across, that’s about ⅓ of the thickness of human hair. You can find silt in soil as well as other types of sediment such as clay, sand, and gravel.

Silt is created when rock is eroded or worn away by water and ice. Flowing water transports tiny rock fragments, and they scrape against the sides and bottoms of the beds of streams, chipping away more rock.
These particles then grind against each other, which makes them smaller and smaller until they are the size of silt.
Rock particles can also be eroded by glaciers to create silt.
Rock particles can also be transported by the wind through a canyon or across a similar landscape, forcing the particles to grind against the canyon wall or one another.
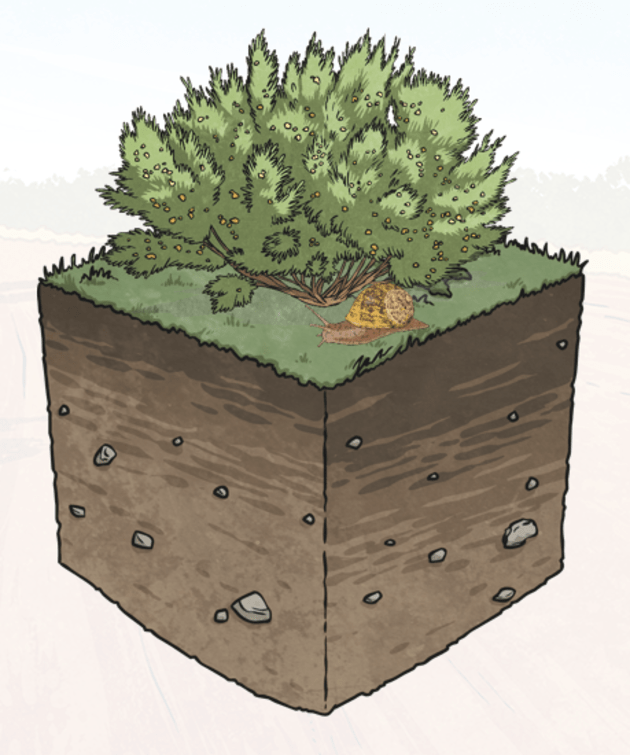
Silt is very small, and can only be seen properly under a microscope or hand lens. You would then be able to recognise silt by its sparkly appearance.
Silt has a non-sticky, plastic feel. Silt usually feels floury when its dry, and it has a slippery feel when its wet.
Silty soils are often used in gardening, they help a lot with water retention in the ground where plants are growing. In places where the ground tends to go dry very quickly, they are commonly added to reduce the need for watering as frequently.
A soil can be called silt if its silt content is greater than 80 percent. Silty soils are made up of fine particles that can be easily compacted by treading and use of garden machinery.
Silty soils are prone to washing away and being eroded by the wind if they are left exposed to the elements without plants to cover them.
Silty soils contain more nutrients than sandy soils and hold more water, so tend to be quite fertile and good for gardening.
Silty soil is usually more fertile than other types of soil, meaning it is good for growing crops. Silt promotes water retention and air circulation. In many parts of the world, agriculture has thrived in river deltas, where silt deposits are rich, and along the sides of rivers where annual floods replenish silt.
When there aren't enough trees, rocks, or other materials to prevent erosion, silt can accumulate quickly. Too much silt can upset some ecosystems.
The Nile River Delta in Egypt is an example of an extremely fertile area of land where farmers have been harvesting crops for thousands of years.
The fertile black silt of the Nile river's banks is a symbol of rebirth, it is associated with the Egyptian god, Anubis.

Silt is able to settle in still water. Deposits of silt can slowly fill places like wetlands, lakes, and harbours.
Floods deposit silt along river banks and on flood plains. Deltas develop where rivers deposit silt as they empty into another body of water.
In some parts of the world, windblown silt covers the land like a blanket. This is known as loess.
Loess landscapes are usually a sign of past glacial activity. A great example of this is the Great Plains, a broad expanse of flatland which can be found in the USA, located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains.
About 60 percent of the Mississippi River Delta is made up of silt.
Many species of organisms thrive in slick, silty soil. Lotus plants take root in muddy, silty wetlands, but their large, showy flowers blossom above water.
Different species of frog hibernate during the cold winter by burying themselves in a layer of soft silt at the bottom of lakes or ponds. The water at the bottom of a pond or lake does not freeze, and the silt provides some insulation, or warmth, for the animals hibernating there.
Lotus flowers are important symbols in Hindu, Buddhist, and ancient Egyptian religions. The lotus flower is the national flower of India and Vietnam.
If you’ve enjoyed learning more about silt, check out these other resources to learn more.
 Home
Home  Membership
Membership  Customer Support
Customer Support  Create
Create  Blog
Blog 









