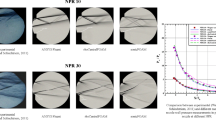
Abstract
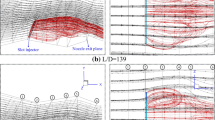
The double divergent nozzle is a type of altitude adaptive nozzle. The double divergent nozzle does not have any mechanical parts, leading to reduced nozzle weight and requires minimum modifications to the existing launch system. The planar double divergent nozzle is a type of double divergent nozzle, having a rectangular cross section. The present study involved the numerical analyses of a single divergent nozzle, and five double divergent nozzle geometries. The flow is simulated on five different double divergent sections having the same area ratio, but with different inflection angles/extension length. All geometries are studied with similar boundary conditions. Flow pattern, wall static pressure, side load, and specific impulse are studied for pressure ratios ranging from 1.5 to 8.5 with cold air as working fluid. The results obtained are compared with a single divergent nozzle having the same area ratio. It is inferred that the flow pattern, side load, and specific impulse of a double divergent nozzle have a strong dependence on the inflection angle.
Graphic abstract





























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A exit :
-
Area of cross section at exit (m2)
- A t :
-
AREA of cross section at throat (m2)
- A inf :
-
Area of cross section at inflection point (m2)
- A w :
-
Surface area of wall
- DBN:
-
Dual bell nozzle
- NPR:
-
Nozzle pressure ratio (P0/Pa)
- NPRwall static :
-
Wall static nozzle pressure ratio (Pw/Po)
- T a :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- P a :
-
Ambient pressure (Pa)
- P w :
-
Wall pressure (Pa)
- SDN:
-
Single divergent nozzle
- DDN:
-
Double divergent nozzle
- RSS:
-
Restricted shock separation
- FSS:
-
Free shock separation
- L b :
-
Length of the base nozzle (mm)
- L e :
-
Length of extension nozzle (mm)
- L :
-
Total length of divergent part (mm)
- θ :
-
Inflection angle
- F l :
-
Force acting on lower wall (N)
- F u :
-
force acting on upper wall (N)
- F :
-
Side load (N)
- I sp :
-
Specific impulse
- V e,b :
-
Average velocity at base nozzle exit plane (m/s)
- P e,b :
-
Average pressure at base nozzle exit plane (Pa)
- V e,e :
-
Average velocity at extension nozzle exit plane (m/s)
- P e,e :
-
Average pressure at extension nozzle exit plane (Pa)
- P e,w :
-
Average base nozzle extension wall pressure (Pa)
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate (kg/s)
References
Arora R, Vaidyanathan A (2015) Experimental investigation of flow through planar double divergent nozzles. Acta Astronaut 112:200–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.03.020
Balabel A, Hegab AM, Nasr M, El-Behery SM (2011) Assessment of turbulence modeling for gas flow in two-dimensional convergent–divergent rocket nozzle. Appl Math Model 35:3408–3422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2011.01.013
Cai G, Fang J, Xu X, Liu M (2007) Performance prediction and optimization for liquid rocket engine nozzle. Aerosp Sci Technol 11:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2006.07.002
Chaudhuri A, Hadjadj A (2016) Numerical investigations of transient nozzle flow separation. Aerosp Sci Technol 53:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2016.03.006
Chien KY (1982) Predictions of channel and boundary-layer flows with a low-Reynolds-number turbulence model. AIAA J 20:33–38. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.51043
Choudhury SP, Suryan A, Pisharady JC, Jayashree A, Rashid K (2018) Parametric study of supersonic film cooling in dual bell nozzle for an experimental air–kerosene engine. Aerosp Sci Technol 78:364–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2018.04.038
Cowles FB, Foster CR, (1949) Experimental study of gas flow separation in over expanded exhaust nozzles for rocket motors, JPL Progress Report 4–103. Jet Propulsion Lab., California Inst. of Tech., Pasadena, CA
Dumnov GE, Nikulin GZ, Ponomaryov NB, (1996) Advanced rocket engine nozzle. In: Proceedings of 32nd joint propulsion conference and exhibit, Lake Buena Vista, Florida. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1996-3221
Fluent User’s Guide (2015) ANSYS Inc., Canonsburg, pp 1–1146
Frey M, Hagemann G (1999) Critical assessment of dual-bell nozzles. J Propuls Power 15:137–143. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.5402
Genin C, Stark RH (2010) Experimental and numerical study on flow transition in dual-bell nozzles. J Propuls Power 26:363–376. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.47282
Genin C, Stark RH (2011) Side loads in subscale dual bell nozzles. J Propuls Power 27:828. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B34170
Génin C, Stark R (2011) Experimental investigation of the inflection geometry on dual bell nozzle flow behavior. In: Proceedings of 47th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE joint propulsion conference & exhibit San Diego, California. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2011-5612
Génin C, Stark R, Haidn O, Quering K, Frey M (2013) Experimental and numerical study of dual bell nozzle flow. Prog Flight Phys 5:363–376. https://doi.org/10.1051/eucass/201305363
Ghasemi E, McEligot DM, Nolan KP, Crepeau J, Siahpush A, Budwig RS, Tokuhiro A (2014) Effects of adverse and favorable pressure gradients on entropy generation in a transitional boundary layer region under the influence of freestream turbulence. Int J Heat Mass Transf 77:475–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.05.028
Hadjadj A, Perrot Y, Verma S (2015) Numerical study of shock/boundary layer interaction in supersonic overexpanded nozzles. Aerosp Sci Technol 42:158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2015.01.010
Hagemann G, Frey M, Koschel W (2002b) Appearance of restricted shock separation in rocket nozzles. J Propuls Power 18:577–584. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.5971
Hagemann G, Immich H, Nguyen TV, Dumnov GE (1998) Advanced rocket nozzles. J Propuls Power 14:620–634. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.5354
Hagemann G, Terhardt M, Haeseler D, Frey M (2002a) Experimental and analytical design verification of the dual-bell concept. J Propuls Power 18:116–122. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.5905
Horn M, Fisher S (1994) Dual-bell altitude compensating nozzles. NASA CR-194719, pp 140–147
Jia R, Jiang Z, Zhang W (2016) Transient three-dimensional side-loads analysis of a thrust-optimized parabolic nozzle during staging. Acta Astronaut 122:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2016.01.023
Kbab H, Sellam M, Hamitouche T, Bergheul S, Lagab L (2017) Design and performance evaluation of a dual bell nozzle. Acta Astronaut 130:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2016.10.015
Kurbatskii K, Montanari F (2007) Application of pressure-based coupled solver to the problem of hypersonic missiles with aerospikes. In: Proceedings of 45th Aiaa Aerospace Sciences Meeting And Exhibit, Reno, Nevada. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2007-462
Launder BE, Sharma BI (1974) Application of the energy-dissipation model of turbulence to the calculation of flow near a spinning disc. Lett Heat Mass Transf 1:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/0094-4548(74)90150-7
Martelli E, Nasuti F, Onofri M (2007) Numerical parametric analysis of dual-bell nozzle flows. AIAA J 45:640–650. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.26690
Menter FR (1994) Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J 32:1598–1605. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.12149
Miyazawa M, Otsu H, (2004) An analytical study on design and performance of dual-bell nozzles. In: Proceedings of 42nd AIAA aerospace sciences meeting and exhibit reno, Nevada. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2004-380
Mousavi SM, Roohi E (2014) Three dimensional investigation of the shock train structure in a convergent–divergent nozzle. Acta Astronaut 105:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.09.002
Nair PP, Suryan A, Kim HD (2017) Computational study of performance characteristics for truncated conical aerospike nozzles. J Therm Sci 26:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-017-0965-0
Nair PP, Suryan A, Kim HD (2019a) Study of conical aerospike nozzles with base-bleed and freestream effects. J Spacecr Rocket 56:990–1005. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A34256
Nair PP, Suryan A, Kim HD (2019b) Computational study on flow through truncated conical plug nozzle with base bleed. Propuls Power Res 8:108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jppr.2019.02.001
Nasuti F, Onofri M, Martelli E (2005) Role of wall shape on the transition in dual-bell nozzles. J Propul Power 21:243–250. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.6524
Nasuti F, Onofri M, (2001) Flow analysis and methods of design for dual-bell nozzles, In: Proceedings of 37th joint propulsion conference and exhibit, Salt Lake City, Utah. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2001-3558
Otsu H, Miyazawa M, Nagata Y (2005) Design criterion of the dual-bell nozzle contour. In: Proceedings of 56th International Astronautical Congress of the International Astronautical Federation, the International Academy of Astronautics, and the International Institute of Space Law Fukuoka, Japan. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.IAC-05-C4.2.08
Papamoschou D, Zill A, Johnson A (2009) Supersonic flow separation in planar nozzles. Shock Waves 19(3):171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-008-0160-z
Papamoschou D, Zill A (2004) Fundamental investigation of supersonic nozzle flow separation. In: Proceedings of 42nd AIAA aerospace sciences meeting and exhibit, Reno, Nevada. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2004-1111
Roache PJ (1994) Perspective: a method for uniform reporting of grid refinement studies. J Fluids Eng 116:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2910291
Ruf JH, McDaniels DM, Brown AM, (2010) Details of side load test data and analysis for a truncated ideal contour nozzle and a parabolic contour nozzle. In: Proceedings of 46th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE joint propulsion conference & exhibit, Nashville, Tennessee. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2010-6813
Ruf JH, McDaniels DM, Brown AM, (2009) Nozzle side load testing and analysis at MSFC. In: Proceedings of 45th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE joint propulsion conference & exhibit 2009 Aug 2, p 4856. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2009-4856
Shine SR, Kumar SS, Suresh BN (2012) Influence of coolant injector configuration on film cooling effectiveness for gaseous and liquid film coolants. Heat Mass Transf 48:849–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0936-z
Shome B (2013) Numerical study of oscillating boundary layer flow over a flat plate using k–kL–ω turbulence model. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 42:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2013.03.002
Soman S, George J, Nair PP, Suryan A (2019) Numerical study of flow through planar double divergent nozzles. AIP Conf Proc 2134:020006. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5120193
Taylor NV, Hempsell CM, Macfarlane J, Osborne R, Varvill R, Bond A, Feast S (2010) Experimental investigation of the evacuation effect in expansion deflection nozzles. Acta Astronaut 66:550–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2009.07.016
Taylor N, Steelant J, Bond R (2011) Experimental comparison of Dual bell and expansion deflection nozzles. In: Proceedings of 47th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE joint propulsion conference & exhibit, San Diego, California. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2011-5688
Thiagarajan V, Panneerselvam S, Rathakrishnan E (2006) Numerical flow visualization of a single expansion ramp nozzle with hypersonic external flow. J Vis 9:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03181572
Tkacik PT, Keanini RG, Srivastava N, Tkacik MP (2011) Color Schlieren imaging of high-pressure overexpanded planar nozzle flow using a simple, low-cost test apparatus. J Vis 14:11–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-010-0056-8
Verma SB, Stark R, Haidn O (2006) Relation between shock unsteadiness and the origin of side-loads inside a thrust optimized parabolic rocket nozzle. Aerosp Sci Technol 10:474–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2006.06.004
Verma SB, Stark R, Haidn O (2012) Gas-density effects on dual-bell transition behavior. J Propuls Power 28:1315–1323. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B34451
Verma SB, Stark R, Haidn O (2013) Reynolds number influence on dual-bell transition phenomena. J Propuls Power 29:602–609. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B34734
Verma SB, Stark RH, Haidn O (2014) Effect of ambient pressure fluctuations on dual-bell transition behavior. J Propuls Power 30:1192–1198. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B35067
Wagner B, Stark R, Schlechtriem S (2011) Experimental study of a planar expansion-deflection nozzle. Prog Propuls Phys 2:641–654. https://doi.org/10.1051/eucass/201102641
Walters DK, Cokljat D (2008) A three-equation eddy-viscosity model for Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes simulations of transitional flow. J Fluids Eng 130:121401. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2979230
Xiao Q, Tsai HM, Papamoschou D (2007) Numerical investigation of supersonic nozzle flow separation. AIAA J 45:532–541. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.20073
Yaravintelimath A, Raghunandan BN, Morinigo JA (2016) Numerical prediction of nozzle flow separation: issue of turbulence modeling. Aerosp Sci Technol 50:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2015.12.016
Zill A (2006) Flow separation in rectangular over-expanded supersonic nozzles. In: Proceedings of 44th AIAA aerospace science meeting and exhibit, Reno Nevada. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2006-17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, J., Nair, P.P., Soman, S. et al. Visualization of flow through planar double divergent nozzles by computational method. J Vis 24, 711–732 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-020-00729-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-020-00729-9