clinoid process
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Legal, Financial, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
Related to clinoid process: cavernous sinus, clivus
process
[pros´es]1. a prominence or projection, as from a bone.
2. a series of operations or events leading to achievement of a specific result.
3. to subject to such a series to produce desired changes.
acromial process acromion.
altered family p's former name for the nursing diagnosis interrupted family processes.
alveolar process the part of the bone in either the maxilla or mandible that surrounds and supports the teeth.
basilar process a quadrilateral plate of the occipital bone projecting superiorly and anteriorly from the foramen magnum.
calcaneal process of cuboid bones a process projecting posteriorly from the inferomedial angle of the cuboid bone that supports the anterior calcaneus.
caudate process the right of the two processes on the caudate lobe of the liver.
ciliary p's meridionally arranged ridges or folds projecting from the crown of the ciliary body.
clinoid process any of three processes of the sphenoid bone (anterior, medial, and posterior).
coracoid process a curved process arising from the upper neck of the scapula and overhanging the shoulder joint; called also coracoid.
coronoid process
1. the anterior part of the upper end of the ramus of the mandible.
2. a projection at the proximal end of the ulna.
disturbed thought p's a nursing diagnosis approved by the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association, defined as the experiencing by an individual of disruption in cognitive operations and activities; it is related to various mental and personality disorders. Contributing factors include physiologic changes, psychologic conflicts, memory loss, impaired judgment, and sleep deprivation. Defining characteristics include inaccurate interpretation of the environment; cognitive dissonance; distractibility; decreased ability to grasp ideas; impaired ability to make decisions, solve problems, or reason; disorientation to time, place, person, circumstances, or events; and inappropriate or nonreality-based thinking.
dysfunctional family p's: alcoholism a nursing diagnosis approved by the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association, defined as psychosocial, spiritual, and physiological functions of the family unit that are chronically disorganized, leading to conflict, denial of problems, resistance to change, ineffective problem solving, and a series of self-perpetuating crises. See also alcoholism.
ensiform process xiphoid process.
ethmoid process a bony projection above and behind the maxillary process of the inferior nasal concha.
family p's the psychosocial, physiological, and spiritual functions and relationships within the family unit; nursing diagnoses include dysfunctional family processes: alcoholism and interrupted family processes.
frontonasal process frontonasal prominence.
interrupted family p's a nursing diagnosis accepted by the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association, defined as a change in family relationships and/or functioning.
malar process zygomatic process of the maxilla.
mammillary process a tubercle on each superior articular process of a lumbar vertebra.
mandibular process mandibular prominence.
mastoid process a conical projection at the base of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.
maxillary process
2. a bony process descending from the ethmoid process of the inferior nasal concha.
nursing process see nursing process.
odontoid process a toothlike projection of the axis that articulates with the atlas.
pterygoid process either of the two processes of the sphenoid bone, descending from the points of junction of the great wings and the body of the bone, and each consisting of a lateral and a medial plate.
spinous process of vertebra a part of a vertebra projecting backward from the arch, giving attachment to muscles of the back.
styloid process a long, pointed projection, particularly a long spine projecting downward from the inferior surface of the temporal bone.
temporal process the posterior blunt process of the zygomatic bone that articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch.
uncinate process any hooklike process, as of vertebrae, the lacrimal bone, or the pancreas.
xiphoid process the pointed process of cartilage, supported by a core of bone, connected with the lower end of the sternum; called also xiphoid.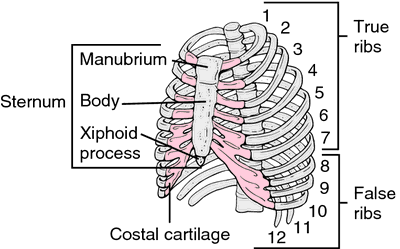

The xiphoid process. Redrawn from Applegate, 1995.
zygomatic process a projection in three parts, from the frontal bone, temporal bone, and maxilla, by which they articulate with the zygomatic bone (see Appendix 3-3).
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
cli·noid pro·cess
[TA]one of three pairs (anterior, middle, and posterior) of bony projections from the sphenoid bone; the anterior and posterior pairs of which surround the hypophysial fossa like bedposts.
Synonym(s): processus clinoideus [TA], clinoid (2)
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
cli·noid pro·cess
(klin'ōyd pros'es) [TA]One of three pairs of bony projections from the sphenoid bone: anterior clinoid process, the recurved posterior angle of the lesser wing; middle clinoid process, a little spur of bone on the body of the sphenoid, posterolateral to the tuberculum sellae; posterior clinoid process, a spur of bone at each superior angle of the dorsum sellae.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012