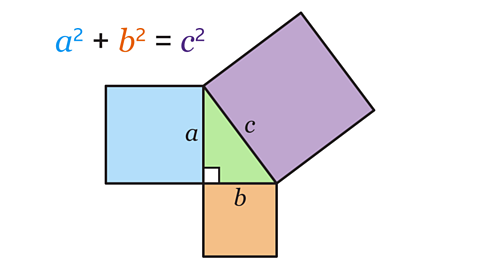
Key points
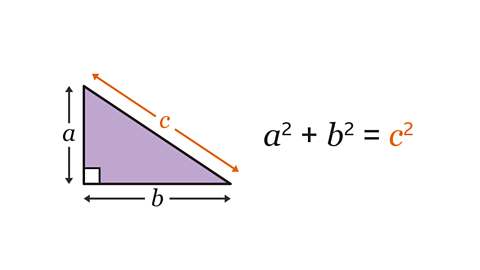
An understanding of how to use Pythagoras’ theorem to find missing sides in a right-angled triangle is essential for applying the theorem in different contexts.
Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to find the distance between two points. This is done by joining the points together to form the hypotenuseThe longest side of a right-angled triangle, which is always opposite the right angle. When labelling a length as the hypotenuse, it can be shortened to 𝒉. of a right-angled triangle and using the theorem \(a\)² + \(b\)² = \(c\)² to find the length of the hypotenuse.
Pythagoras’ theorem can also be used to find missing lengths in shapes, such as rectangles and isosceles triangleA triangle with two equal sides. This means two angles are equal. once the shape has been split into right-angled triangles.
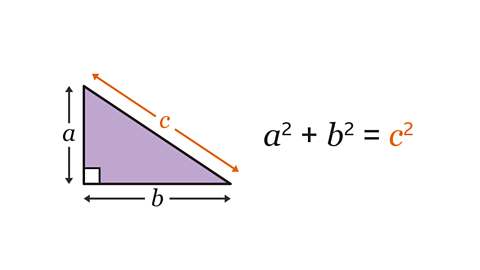
How to find the distance between two points
Follow these steps to calculate the distance between two coordinatesThe ordered pair of numbers (𝒙, 𝒚) that defines the position of a point is the coordinate pair (or the coordinates.) on a set of axesTwo reference lines, one horizontal and one vertical, that cross at right-angles. They are used to define the position of a point on a grid. Axes is the plural of axis. . The same steps can be taken to calculate the length of a line segmentA specific part of a line between two points. where the two end points are the two coordinates.
- Join the two coordinates with a straight line. This will become the hypotenuseThe longest side of a right-angled triangle, which is always opposite the right angle. When labelling a length as the hypotenuse, it can be shortened to 𝒉. of a right-angled triangle and is the length that needs to be found.
- Draw a horizontalA line that is parallel to the horizon. and verticalA line that is perpendicular to the horizon. line from the two coordinates to form a right-angled triangle.
- Calculate the horizontal length of the triangle by finding the difference between the x-coordinates. This is side a of the right-angled triangle.
- Calculate the vertical length of the triangle by finding the difference between the y-coordinates. This is side b of the right-angled triangle.
- Substitute the values of \(a\) and \(b\) into Pythagoras’ theorem: \(a\)² + \(b\)² = \(c\)².
- Add the squares together, then find the square root to calculate the c, the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is the distance between the two points.
Example
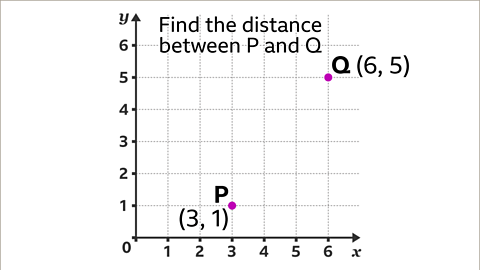
Image caption, Find the distance between the points P and Q.
Image caption, (3,1) is the coordinate that is 3 along the x-axis, and 1 up the y-axis. (6,5) is the coordinate that is 6 along the x-axis, and 5 up the y-axis. The line segment PQ is the line between the two points P and Q. Join the two coordinates to make a line segment.
Image caption, Draw a horizontal line (going across) from P, and a vertical line (going down) from point Q, to form a right-angled triangle.
Image caption, The width of the triangle is the difference between the x-coordinates 3 and 6. The width is 6 – 3 = 3
Image caption, The height of the triangle is the difference between the y-coordinates 1 and 5. The height is 5 – 1 = 4
Image caption, Pythagoras’ theorem can now be used on the right-angled triangle to calculate the length PQ. PQ is the hypotenuse so should be labelled 𝒄, and the other two sides should be labelled 𝒂 and 𝒃. It does not matter which way round 𝒂 and 𝒃 are labelled. Substitute the values of 𝒂 and 𝒃 into the formula 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄² to give the equation 3² + 4² = 𝒄².
Image caption, Add 9 + 16 together to give the value of 𝒄² = 25. To find the value of 𝒄, calculate the square root of 25. This gives the final answer of 𝒄 = 5, therefore PQ = 5
1 of 7
Question
Find the distance between points R and S.
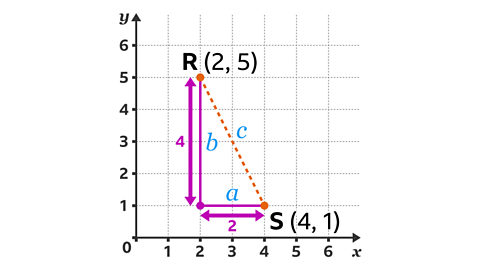
Draw a horizontal and vertical line from the two coordinates to form a right-angled triangle.The width of the triangle is 2
This can be labelled \(a\).
The height of the triangle is 4
This can be labelled \(b\).
The line segment RS is labelled \(c\).
Substitute the values of a, b and c into Pythagoras’ theorem to give 2² + 4² = \(c\)².
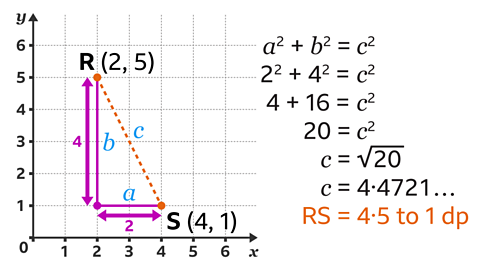
4 + 16 = 20
To find the value of \(c\), calculate the square root of 20
This gives the final answer of \(c\)² = 4.4721… which rounded to one decimal place = 4.5
Therefore, the distance between R and S is 4.5
Applying Pythagoras’ theorem to other shapes
Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to find the diagonal of a rectangle. The width and height of the rectangle become \(a\) and \(b\) in the formula and \(c\) is the diagonal length.
\(a\)² + \(b\)² = \(c\)²
isosceles triangleA triangle with two equal sides. This means two angles are equal. can be split into two right-angled triangles. This means Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to find the lengths of missing sides, such as the perpendicularPerpendicular lines are at 90° (right angles) to each other. height. It is important to remember that when an isosceles triangle is cut in half this way, the base length is also cut in half.
Examples
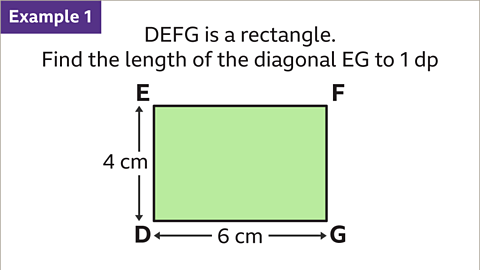
Image caption, Find the length of the diagonal EG to 1 decimal place (1 dp).
Image caption, The diagonal EG is the line that goes from E to G. This creates two right-angled triangles.
Image caption, Taking the triangle DEG, Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to calculate the length of EG. EG is the hypotenuse so should be labelled as 𝒄. ED can be labelled as 𝒂. DG can be labelled as 𝒃. Substitute the values of 𝒂 and 𝒃 into the formula 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄² to give the equation 4² + 6² = 𝒄², 16 + 36 = 52. To find the value of 𝒄, calculate the square root of 52. This gives the final answer of 𝒄 = 7.211... When rounded to 1 decimal place, the length of the diagonal EG is 7.2 cm.
Image caption, Find the perpendicular height of the isosceles triangle.
Image caption, An isosceles triangle has two sides of the same length (25 cm). The perpendicular height is the height at a right angle to the base of the triangle. The isosceles triangle can be split into two right-angled triangles. Pythagoras’ theorem can then be used on either of the two right-angled triangles. The 25 cm length becomes the hypotenuse so should be labelled 𝒄. The base of the isosceles triangle has been cut in half, so is 7 cm. This can be labelled as 𝒂. The height can be labelled as 𝒃.
Image caption, Substitute the values of 𝒂, 𝒃 and 𝒄 into the equation 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄². 𝒂² = 7² and 𝒄² = 25². 𝒃² is not known. This leads to the equation 7² + 𝒃² = 25². Calculate the value of the squares. 7² = 49, and 25² = 625. This leads to the equation 49 + 𝒃² = 625. To work out the value of 𝒃², subtract 49 from both sides of the equation. This leads to the equation 𝒃² = 576. The inverse of squaring is square rooting, so to find 𝒃, calculate the square root of 576. This gives the answer of 𝒃 = 24. Therefore, the height of the triangle is 24 cm.
Image caption, Calculate the length of 𝒙, the base of the isosceles triangle.
Image caption, The isosceles triangle can be split into two right-angled triangles. The base of the isosceles triangle has been cut in half, so the base of the right-angled triangle is given a different letter, 𝒚. 𝒚 is half of 𝒙. Pythagoras’ theorem can then be used on either of the two right-angled triangles. The 3.4 m length becomes the hypotenuse so should be labelled 𝒄. The height is 3 m, and can be labelled as 𝒂. The base of the right-angled triangle can be labelled as 𝒃.
Image caption, Substitute the values into the equation 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄². 𝒂² = 3² and 𝒄² = 3.4². 𝒃² can be substituted with 𝒚² . This leads to the equation 3² + 𝒚² = 3.4² . Calculate the value of the squares. 3² = 9, and 3.4² = 11.56. This leads to the equation 9 + 𝒚² = 11.56. To work out the value of 𝒚² , subtract 9 from both sides of the equation. This leads to the equation 𝒚² = 2.56. The inverse (opposite) of squaring is square rooting, so to find 𝒚, calculate the square root of 2.56. This gives the answer of 𝒚 = 1.6cm. However, this is not the final answer.
Image caption, The aim is to find the base of the isosceles triangle, 𝒙. The base of each right-angled triangle is 1.6 cm. 𝒙 is double this length. 𝒙 = 2 x 1.6 = 3.2 cm.
1 of 10
Question
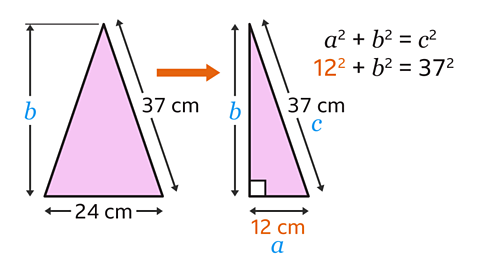
A question asks to calculate the height of the isosceles triangle, \(b\). The start of the working is shown on the right.
What mistake has been made?
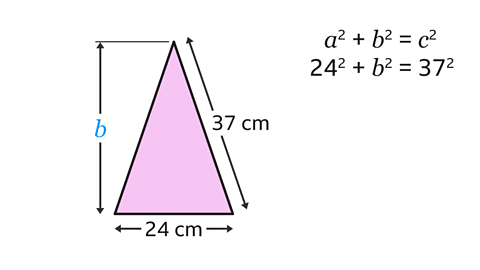
The lengths of the isosceles triangle have been used in the equation. However, Pythagoras’ theorem only works for right-angled triangles.
The isosceles triangle needs to be split into two right-angled triangles. The width of the right-angled triangle is 12 cm. 12 cm is the correct value for \(a\) (not 24 cm).
The correct equation is 12² + \(b\)² = 37².
Visual proof of Pythagoras' theorem
Explore a visual way of showing Pythagoras’ theorem below.
Example
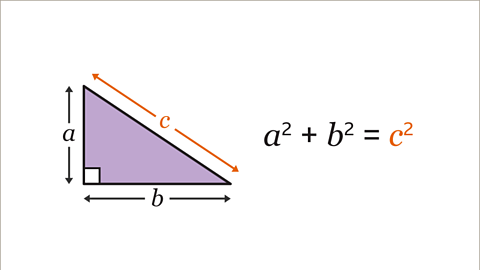
Image caption, This triangle will be used to show Pythagoras’ theorem that 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄². The hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is labelled as 𝒄. The other two sides are labelled 𝒂 and 𝒃.
Image caption, The whole square is made up of 4 right-angled triangles with lengths 𝒂 and 𝒃, and 2 squares. The area of the top square is 𝒂 x 𝒂 = 𝒂². The area of the bottom square is 𝒃 x 𝒃 = 𝒃².
Image caption, The four triangles can be rearranged to make the diagram on the right. The length of the hypotenuse of each triangle is 𝒄. The area of the orange square is 𝒄 x 𝒄 = 𝒄².
Image caption, The diagram on the left contains four right-angled triangles, and two squares (with areas 𝒂² and 𝒃²). The diagram on the right contains the same four right-angled triangles, and one square (with area 𝒄²).The two squares on the left (with areas 𝒂² and 𝒃²) must take up the same amount of space as the square on the right (with area 𝒄²). Therefore, 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄².
Image caption, The diagram on the left contains 4 right - angled triangles, and two squares ( with areas 𝒂² and 𝒃².) The diagram on the right contains the same 4 right - angled triangles, and one square ( with area 𝒄²). The two squares on the left ( with areas 𝒂² and 𝒃²) must take up the same amount of space as the square on the right ( with area 𝒄²). Therefore, 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄².
1 of 5
Practise using Pythagoras' theorem
Quiz
Practise calculating different lengths of sides using Pythagoras' theorem with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Real-life maths

Navigation systems on ships use Pythagoras’ theorem to calculate the shortest distance to a certain destination.
Knowing the ship’s coordinates and the coordinates of their destination means they can find the distance between those two points.
It is vital to know this distance to check if the ship has enough fuel to get to its destination safely.

Game - Divided Islands
Divided Islands. gameDivided Islands
Use your maths skills to help the islanders of Ichi build bridges and bring light back to the islands in this free game from BBC Bitesize.

More on Pythagoras and trigonometry
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 5
- count1 of 5