In modern manufacturing, a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is really important. It helps coordinate and control production processes with great accuracy.
It is like the digital brain of the factory floor, making sure everything runs smoothly. It helps industries manage their resources better, make sure the quality is good, and make decisions based on data.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss the meaning, functionalities, and advantages of MES. We will also explore implementation best practices and the difference between MES and ERP. So read on to learn more about it and how it can help your business.
What is MES?
A Manufacturing Execution System serves as the central control hub of a manufacturing operation, overseeing and coordinating every aspect of the production process.
It acts as a diligent manager, monitoring and managing production activities, inventory levels, equipment utilization, and workforce allocation to ensure optimal efficiency and productivity.
It collects data from the production line and other sources and provides it to operators, managers, and planners to make better product production decisions.
It can help companies improve quality, efficiency, and throughput. It can also help them respond quickly to customer demands and changes in market conditions.
For example, if there is a sudden increase in customer demand for a product, the system can help the company quickly ramp up production to meet the demand.
Conversely, if there is a drop in demand, the system can help the company reduce production to avoid excess inventory. In this way, it can help companies be more agile and responsive to changes in market conditions.
Functionalities
It provides a wide range of benefits for manufacturers. For example, integrating with ERP systems gives organizations a real-time view of production, making it possible to identify and address issues as they arise quickly.
In addition, it provides extensive data collection and analysis capabilities, allowing organizations to track performance and identify areas for improvement.
Additionally, it can help manage quality control, ensuring that products meet the highest standards.
Finally, it can also provide valuable insights into maintenance needs, helping to reduce downtime and improve overall equipment efficiency. By leveraging the power of MES, manufacturers can experience significant improvements in productivity and quality.
Basic/MESA-11 Model Features
These features were defined by the Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association International (MESA) in 1997.
- Operations/detailed scheduling: Depending on the resource capacity and priority, scheduling, sequencing, and timing of the activities enhance the performance.
- Allocation of resources and status: Tracking and analyzing the resource status (machines, labor, materials) using real-time data.
- Dispatching production units: Monitoring and managing the real-time production data flow for calculating the adjustments in production dispatching.
- Document control: Management of documents such as work instructions, standard operation procedures (SOP), drawings, batch records, etc.
- Labor management: Monitoring work schedules, employment qualifications, and authorizations to enhance the labor management system with fewer resources and time.
- Data collection and acquisition: Collect and track real-time information about materials, equipment, processes, and operations to make good decisions and enhance efficiency.
- Process management: Production process management from order release to final product manufacturing. Identifying the production bottlenecks that impact the quality of the production.
- Quality management: Monitoring of quality loopholes, management, and documentation
- Maintenance management: Using manufacturing execution systems data to determine equipment issues before they cause damage. Adjustment of machine and equipment schedules to increase production efficiency and decrease downtime.
- Product tracking and genealogy: Tracking product improvement and genealogy to make better decisions. Collecting product history to comply with industry standards or government regulations.
- Performance analysis: Performance analysis compares output results and goals to determine the process’s strengths and weaknesses.
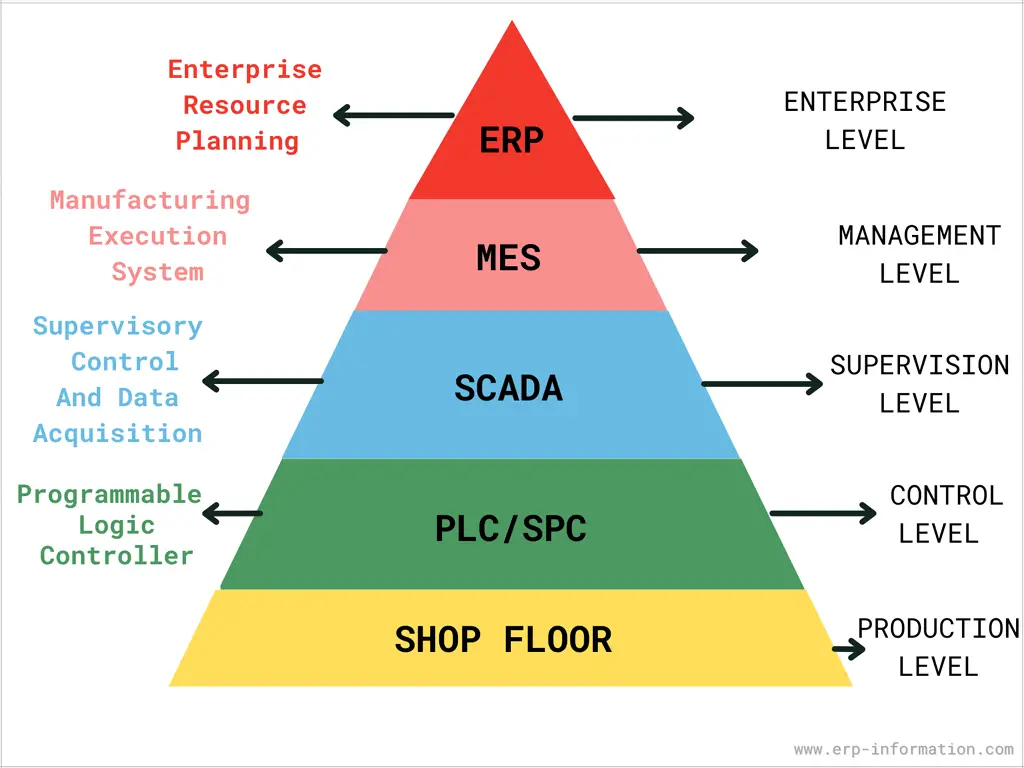
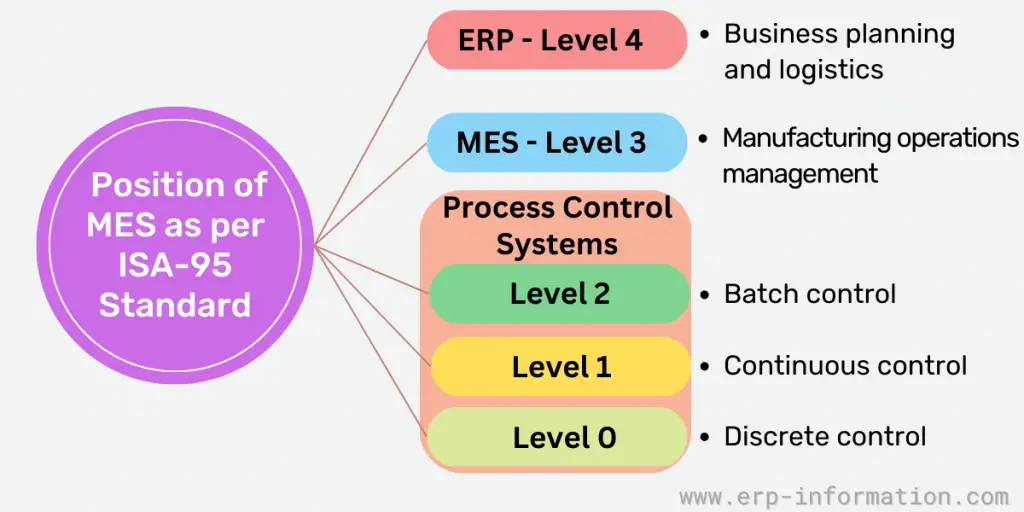
MES Position as per ISA-95 Standard
MESA-11 focused only on the basic features of MES, but the International Society of Automation (ISA) included terminology and defined the activities between the control system and enterprise. So it established the ISA-95 standard in the 1990s.
The position of the MES as per ISA-95 standard is as follows.
- Level 4 – ERP: Business planning and logistics
- Level 3 – MES: Manufacturing operations management
- Level 2 – Process control systems: Batch control
- Level 1 – Process control systems: Continuous control
- Level 0 – Process control systems: Discrete control
Advantages of Manufacturing Execution System
- This process is helpful for industries including semiconductors, automotive, pharma companies, aerospace, etc.
- It gathers valuable data on the production line. Hence you can upgrade your manufacturing process.
- Allows you to manage your machines and employees in an easier way.
- It helps to eliminate human error in the manufacturing process.
- It monitors manufacturing activities throughout the industry and links them in lead time.
- It helps to control the manufacturing supply chain.
- Improves the quality of the product by providing real-time quality data checks.
- Eradicates valueless activities like paperwork
- It helps to find the faults easily.
- Supports complicated workflow processes.
- Reduces manufacturing cycle time and data entry time.
- It helps to improve delivery performance and customer service.
Manufacturing Execution System History
Around the 1970s, some manufacturing industries started using software applications to automate their accounts.
Time files and these applications improved and provided particular features for standard inventory management.
In the early 1980s, manufacturing requirements planning (MRP) came with material planning, control, and monitoring.
In the 1990s, the system improved, and the manufacturing execution system came into the picture.
Best Practices for Implementation
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best practices for MES implementation will vary depending on the specific needs of your business. However, some tips to consider include:
- Define clear rules to implement the project.
- Defining the rules involves the production, quality, execution, maintenance, and IT department members throughout the rule-making process.
- Involve stakeholders during the implementation process.
- Set an achievable schedule for implementation and testing.
- Originate a detailed MES system per user requirements with a distance between the control and enterprise resource planning (ERP) layers.
- Perform risk management for design, development, and deployment stages.
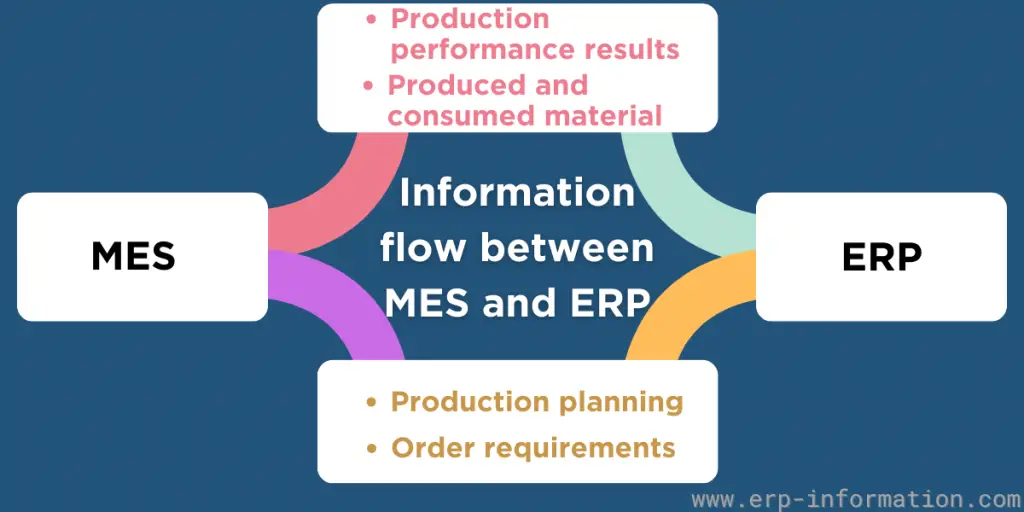
- Determine the merging points between the layers to comprise your architecture. For example, MES stands for execution, and ERP stands for planning. So ERP directs the MES on what to make, and MES tells what was made and where it went.
- Combine the MES software with other production control systems.
Common Mistakes During Implementation
- Not giving attention to the connection of MES requirements with particular business drivers.
- Skipping the steps while getting into the details of master data ownership, the interface points to the control system in the designing stage.
- Improper determination of user requirements.
- Not reviewing the design before implementation. If you review the design before only, you can make the changes before the implementation.
- Improper establishment of the existing operating system. If you do not establish the current operating system, it is not easy to compare and find out the benefits of the MES system.
- Not evaluating the system after implementation. Before switching over entirely to the new system, It is necessary to test the system, even if you implement it as per the plan.
Applications of MES in Various Industries
Manufacturing Execution Systems are used in a wide variety of industries to improve production efficiency, quality, and compliance. Here are some specific examples of how MES is used in various industries:
Industries
- Automotive
- Semiconductor
- Pharmaceutical
- Food and beverage
- Medical devices
- Aerospace and defense
- Metals and plastics
Automotive
Tracks the movement of vehicles through the assembly line, ensures that the correct parts are installed, and monitors the quality of the vehicles at each stage of production.
Semiconductor
Used to track the movement of wafers through the fab, ensure that the correct materials and equipment are used, and monitor the quality of the chips at each stage of production.
Pharmaceutical
PharmaceuticalUsed to track the movement of ingredients and products through the plant, ensure that all manufacturing procedures are followed precisely, and monitor the quality of the products at each stage of production.
Food and beverage
Monitors the movement of materials and products through the plant, ensures that product quality is good at each stage of production and all food safety regulations are followed.
Medical devices
Utilized for monitoring the progress of medical devices during manufacturing, ensuring adherence to quality standards, and complying with governmental regulation
Aerospace and defense
Used to track the movement of aircraft parts through the manufacturing process, ensure that all quality standards are met, and maintain compliance with government regulations.
Metals and plastics
Utilized for tracking raw materials and finished products during manufacturing, ensuring compliance with quality standards, and meeting environmental regulations.
Manufacturing Execution System Software
MES software can track production status, manage inventory, monitor quality control measures, and provide real-time reports. It can also help connect different parts of the manufacturing process to have the same understanding of what’s happening on the shop floor.
The following are a few popular Manufacturing Execution System Software,
- Odoo
- Mar-kov
- Quantum
- Tulip platform
- Tavant Warranty
- MIE Trak pro
- Pro Shop
- Genius ERP
- Prodsmart
MES Integration With ERP
MES and ERP integration is the process of connecting manufacturing software systems to enable real-time data sharing.
This integration provides numerous advantages, including improved production efficiency, enhanced quality control, compliance with industry regulations, reduced costs, and enhanced operational visibility.
There are different methods for integrating MES and ERP systems, such as point-to-point integration, enterprise application integration (EAI), and cloud-based integration.
The choice of integration method depends on the manufacturer’s specific needs and the capabilities of their systems.
To successfully integrate MES and ERP systems, it is essential to make an assessment and keep in mind certain conditions such as choosing the appropriate integration method, and collaborating with an experienced integrator.
This will aid the manufacturers in boosting their operational efficiency, streamline workflows, and make well-informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
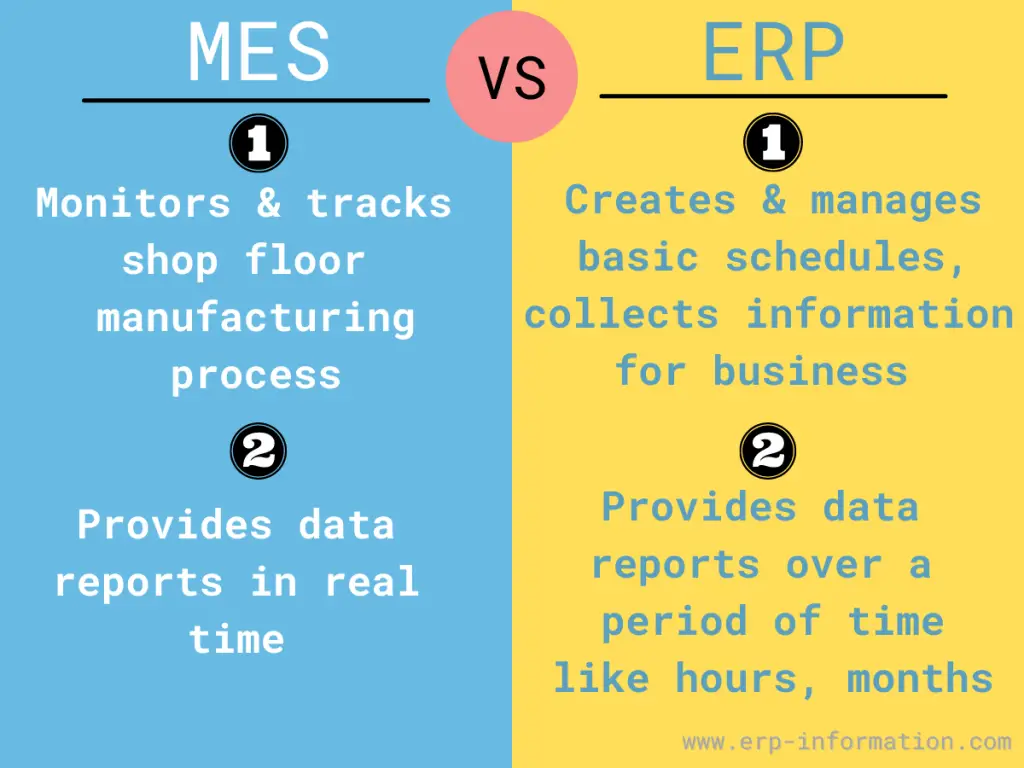
Difference Between MES and ERP
MES stands for Manufacturing Execution System, while ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. MES is focused on the execution of manufacturing operations, while ERP is a broader system that incorporates financials, HR, and other aspects of the business.
MES systems are typically used to manage production processes and track resources (e.g., machines, tools, people). In contrast, ERP systems include modules that can provide these same functionalities and cover other aspects of the business, such as sales and marketing, accounting, and purchasing.
The significant difference is that Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) creates and manages your basic schedules for production, material use, delivery, and shipping and helps collect information for your business.
ERP system is a mixture of many modules like production, supply chain, order processing, inventory management, customer relationship management, and human resource management. Usually, it concentrates on working within the time limit of months, weeks, and days.
It helps monitor and track your shop floor manufacturing process and allows you to generate real-time reports on production plant activities.
You can calculate human resources using our Online Human Resource Calculator
FAQs
What is the MES, and what does it do?
It is a software system that enables the monitoring and execution of manufacturing processes and tasks.
It helps to ensure that products are manufactured according to specifications. It also helps to improve productivity and quality by providing real-time information on the status of production processes. Additionally, it can help identify and correct process problems before they cause product defects.
How does the MES help businesses improve their operations and efficiency?
It helps businesses improve their operations and efficiency by providing a comprehensive view of the manufacturing process.
This allows companies to identify and resolve issues quickly, improving production times and reducing waste.
Additionally, it can help enterprises optimize their production schedules and staffing requirements, ensuring that they efficiently use their resources.
What are some benefits of using an MES system in a manufacturing plant or business environment?
It can help improve the quality of products being manufactured while also helping to improve the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
It can also help improve communication within a business environment by providing a single system that all departments within a company can use.
This can help ensure everyone is on the same page regarding production goals and targets.
Are there any downsides to using an MES system in business operations?
It can improve business operations by increasing efficiency and accuracy and reducing waste. However, using it in your business can have some potential downsides.
One potential downside is that it can be expensive to implement and maintain. Another potential downside is that it can require significant changes to how a business operates, which can be challenging to implement and cause disruptions in production.
Additionally, an MES system can increase the waste a company produces if not implemented correctly.
How can you decide if an MES system suits your company’s needs and goals?
It depends on the company’s needs and goals. It can help a company improve productivity, increase efficiency, and achieve better quality control.
To decide if it is suitable for your company, you should assess your current situation and identify which areas could use improvement.
What are the primary functions of MES in a manufacturing environment?
MES primarily functions to schedule production, track work-in-progress, enforce quality control, monitor equipment and personnel performance, and provide real-time data for decision-making, all while ensuring that production processes are efficient and aligned with customer demands.
What role does MES play in ensuring product quality and consistency in manufacturing?
MES enforces quality standards, tracks production data, and provides real-time quality checks, ensuring products meet specified standards. It offers traceability for process improvement and defect prevention.
What are the key components and modules commonly found in MES software systems?
Common MES modules include production scheduling, quality management, inventory management, equipment maintenance, and performance analytics. Components often include user interfaces, data collection devices, and database systems.
What is the future of MES, and how is it evolving with emerging technologies like IoT and AI?
It is evolving with IoT and AI, offering real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and greater automation. The future of MES lies in its ability to integrate with smart manufacturing technologies.
What industries benefit the most from MES implementation?
Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and pharmaceuticals benefit greatly from MES. However, it can be adapted to various industries, with its relevance depending on specific operational needs.
Conclusion
MES is a system that helps manufacturers automate and control production. It collects data from all the machines in a factory or company to track how efficiently they operate.
Machine performance, quality of raw materials being used for manufacturing, and inventory levels can be monitored, which helps companies optimize their operations by reducing waste and increasing profitability.