Unicast vs Multicast Clustering
When it comes to clustering, there are two main types: unicast and multicast. Each type of clustering has its own unique benefits and drawbacks, so it's important to understand the differences between them.
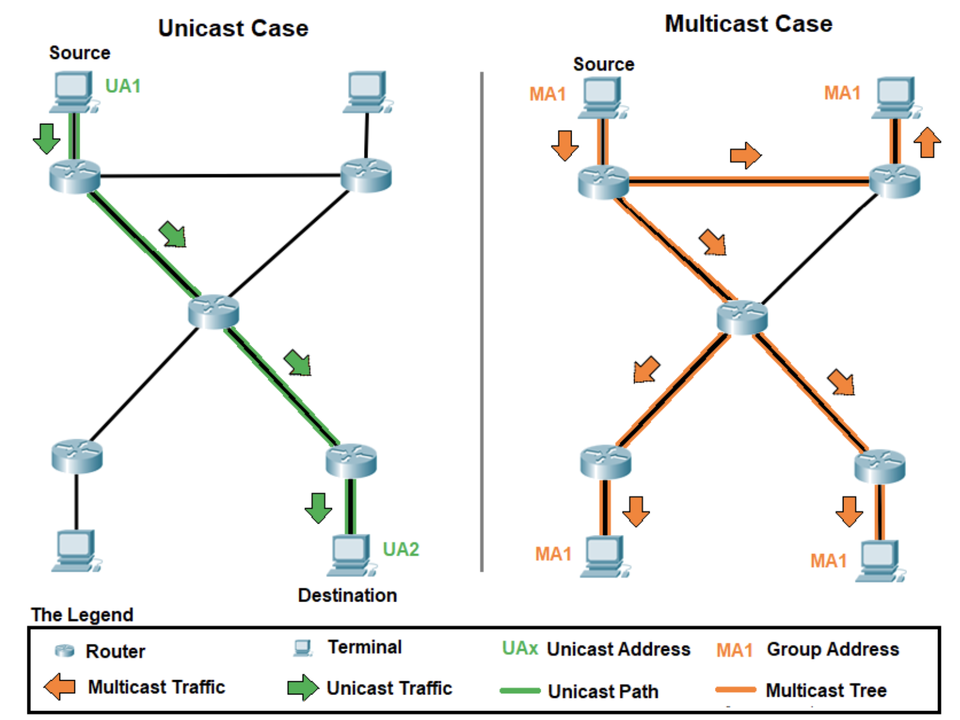
Unicast clustering involves creating a network of nodes that communicate with each other directly. This means that each node is aware of the other nodes in the network and can communicate with them individually. Unicast clustering is typically used in smaller networks where the number of nodes is limited.
Multicast clustering, on the other hand, involves creating a network of nodes that communicate with each other through a multicast IP address. This means that each node sends messages to a single multicast address, which is then received by all other nodes in the network. Multicast clustering is typically used in larger networks where the number of nodes is greater.
The main advantage of unicast clustering is that it provides more control over the network, as each node is aware of the other nodes and can communicate with them directly. This makes it easier to manage and troubleshoot the network. However, unicast clustering can become more complex as the number of nodes in the network grows.
The main advantage of multicast clustering is that it is more efficient, as messages are sent to a single multicast address rather than being sent individually to each node in the network. This makes it ideal for larger networks with many nodes. However, multicast clustering can be more difficult to manage and troubleshoot, as it relies on a single multicast address for communication.
In summary, both unicast and multicast clustering have their own unique benefits and drawbacks. The choice between them depends on the specific needs of your network and the number of nodes involved.