Preventive Healthcare
Exploring Thrombus and Thrombosis: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
1104 Views
0
Introduction
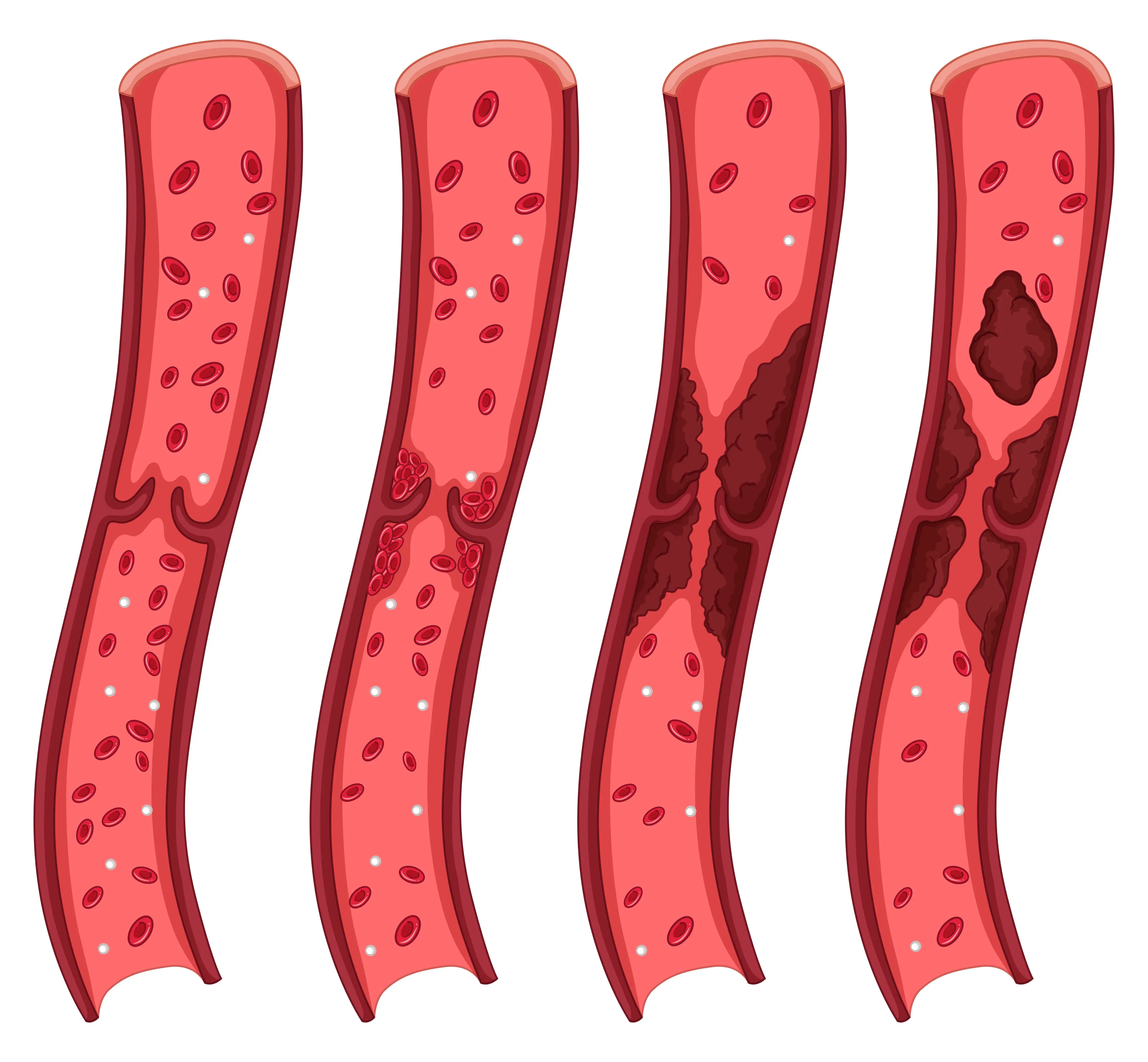
A thrombus is a type of blood clot that develops inside a blood vessel and does not travel to any other site, unlike an embolism. Thrombi (plural for thrombus) lodge itself into a blood vessel and hampers the blood flow through that vessel, blocking the normal blood flow and oxygen from the other tissues. Lack of blood flow results in the destruction of the cells, and cell damage and could also cause cell death or necrosis in that area. The development of a thrombus is referred to as thrombosis.
Types of Thrombi
A blood clot is usually formed in response to a physical injury. The platelets in the blood quickly clot to form a plug at the injury site and prevent bleeding. However, a thrombus interrupts the normal functioning of the blood vessel. If a section of the thrombus breaks off and travels to other body areas, it causes an embolism. This embolism can lodge itself in different body parts but can be exceptionally dangerous if they reach vital organs like the lungs, heart, or brain.
A thrombus is classified on the bases of which blood vessel they develop in
- Arterial thrombosis: A thrombus formed in the artery, especially in the brain or heart, is known as arterial thrombosis. The arteries carry blood from your heart to the other parts of your body. Arterial thrombosis is one of the leading causes of strokes and heart attacks.
- Venous thrombosis: A thrombus formed in a vein is called venous thrombosis. The veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart. A typical example of this kind of blood clot is when it happens deep inside the vein in a disorder called deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Causes of Thrombus
A clot can be caused by a series of chemical reactions in the blood cells called proteins and platelets. When you are healthy, your body can regulate its clotting process according to its needs. However, the probability of developing a thrombus can increase when you are not in the best health. It can be found in individuals who:
- Use tobacco excessively
- Are overweight or have obesity
- Has high cholesterol
- Is overly stressed
- Has a sedentary or inactive lifestyle
- Has cancer
Conditions like atrial fibrillation, coronary artery diseases, diabetes and clotting disorders like antiphospholipid syndrome can also cause thrombosis.
Diagnosis of thrombosis
If your doctor suspects thrombosis, several diagnostic tests can help confirm the condition:
- Blood tests: Your doctor may recommend a blood test called D Dimer Test to check for the presence of a protein fragment called 'D-dimer.' This fragment is typically present when a blood clot starts to dissolve.
- Ultrasound scans: This non-invasive imaging technique can show if there are any blood clots in the veins.
- CT (computed tomography) scanning with intravenous dye: In some cases, your doctor may recommend a CT scan with the use of intravenous dye to check for pulmonary embolism (PE). The dye helps highlight any blockages or abnormalities in the arteries supplying blood to the lungs.
- Ventilation-perfusion scans: These scans involve using radioactive compounds to visualise parts of the lungs that are not receiving adequate oxygen and blood flow. These diagnostic tests play a crucial role in helping doctors accurately diagnose thrombosis and determine appropriate treatment plans based on their findings.
Symptoms of thrombosis
The symptoms of thrombosis depend on the location and size of the thrombus as well as the complications that it may cause. Most blockages occur in smaller blood vessels like the brain, lungs, legs, or arms. Here are a few of the symptoms of a thrombus based on its location:
Lungs
A thrombus in the lungs can cause a pulmonary embolism, the symptoms of which include
- Sharp pain in the chest and surrounding areas including the neck, jaws, shoulders, arms and back
- Pain while breathing
- Breathing trouble when active and sometimes even at rest
Neck or brain
Thrombi in the brain or neck can cause a stroke or transient ischemic attack. These symptoms include:
- Slurring or garbled speech
- Weakness or difficulty in controlling one side of the body
- A noticeable droop on one side of the face
- Agitation, confusion, or any unusual changes in behaviour
Heart
A blockage in the heart results in a heart attack and can display symptoms like
- Discomfort or severe pain in the chest
- Dizziness or fainting
- Trouble breathing
Stomach
A thrombus in the stomach can cause mesenteric ischemia. Early signs of this include
- Bloating, vomiting and nausea
- Diarrhoea can also include blood
- Fever
- Severe stomach or abdominal pain, especially after a meal
Artery in the leg or arm
- Pale skin in some areas
- The skin may feel cool to the touch
- Tingling or numbness
- Wounds, sores and blisters
- Sloughing skin is a result of the skin falling away from the tissue under it
- Necrosis or tissue death
A vein in the legs or arms
- Skin looks darker or redder in some areas
- It can cause pain in certain affected areas
- Fluid buildup resulting in swelling
- Skin that is warm to the touch
Treatment for thrombus
The treatment of thrombus includes medication, surgeries and minimally invasive procedures. These can include:
- Blood thinners keep your blood from clotting easily; while they cannot get rid of an existing clot, they can prevent it from growing.
- Thrombolytic treatments use medication to dissolve any blood clots. However, these are primarily used in emergencies as they can accommodate a thrombus in critical areas like the heart or brain.
- Thrombectomy is a direct way of removing a clot. The surgeon may opt for a minimally invasive technique or open surgery.
In case of complications arise due to thrombosis, you may have to undergo additional treatment as and when needed.
How to take care of yourself if you have a thrombus?
There are certain things you can do if you already have been diagnosed with a thrombus:
- Ensure you take your medications regularly.
- Meet your doctor often.
- Make lifestyle changes needed to fix the root cause of the clot.
- Connect with others in similar conditions.
Book D Dimer Test
Conclusion
Thrombosis is a condition that is unpredictable and can quickly become life-threatening. One needs to do everything in their control to prevent a thrombus from developing, but if already developed, it is essential to ensure the situation doesn't deteriorate. Have a line of open communication with your doctor and ask them anything you may want to know about this condition.
Regular health checkups and blood tests can help you identify early signs of the disorder and help you take preventive actions whenever possible. Metropolis Labs helps its customers with at-home sample collection and accurate results so you can get your necessary blood and body fluid tests down without disrupting your routine. Read more about the various tests offered at their website.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload











1701259759.webp)









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp