Answer
362.4k+ views
Hint: Oocyte is an immature egg cell that matures to form the female gamete- ovum or egg. The maturation of the oocyte occurs in the ovaries.
Complete answer:
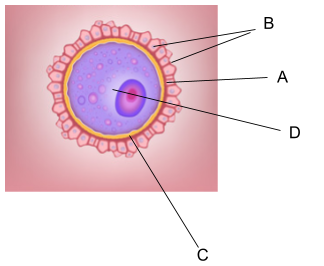
The given figure is the diagram of a primary oocyte. In primary oocytes, the nucleus is large and present in the center.
The oocytes are the immature female gametes that mature in an ovary, within a follicle to form the mature female gamete- ova or egg. The process of formation of ova or egg in the females is called Oogenesis. It begins in the early embryonic period in the females, from the 7th week of gestation. The oogonium is formed from the primordial germ cells and increase in number through mitotic cell division. The oogonium grows till the 5th month of the pregnancy, and no new oogonium- is further added. A large number of these cells degenerate till birth. The maturation of these cells occurs to form the- primary and the secondary oocyte. The secondary oocyte splits into two cells in the second meiotic division- an ootid and a polar body. At the time of ovulation, one ootid is released from the follicle, which matures into an ovum when a sperm penetrates it. The fusion of the two gametes results in the formation of a diploid zygote.
The various structures seen in a primary oocyte are-
1)Corona Radiata- It is a layer formed by follicle cells and has a multicellular thickness. It derives itself from the cumulus oophorus cells- and provides vital proteins to the cells. It is present adjacent to the zona pellucida.
2)Zona Pellucida- It is formed by the secretions of oocytes and follicular cells. It is made up of glycoproteins and surrounds the plasma membrane of the oocyte.
3)Follicular cavity- The appearance of a follicular cavity or antrum- in an oocyte indicates the development of a secondary follicle from the primary follicle. This cavity is filled with follicular fluids and provides a microenvironment for the development of the oocyte.
4)Perivitelline space- The space found between the zona pellucida and the cell membrane of an oocyte is called the- perivitelline space.
5)Germinal Vesicle- It is the enlarged nucleus of the egg that contains the chromatin and nucleolus.
Let us analyze the options to find the correct answer.
Arrow A) points towards the- zona pellucida of the oocyte.
Arrow B) points towards the- corona radiata of the oocyte.
Arrow C) points towards the- perivitelline space of the oocyte.
Arrow D) points towards the- germinal vesicle of the oocyte.
Option E): A- Zona pellucida, B- Corona radiata, C- Perivitelline space, D- Germinal Vesicle is the correct option.
All the other options are irrelevant.
Hence, the correct answer is option (E)
Note: The primary oocytes remain arrested in the- Prophase stage of Meiosis I after birth. They resume Meiosis during puberty or sexual maturity. During each menstrual cycle- a set of primary oocytes resumes the process of Meiosis I to develop into a secondary oocyte after the action of various hormones like- FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone
Complete answer:
The given figure is the diagram of a primary oocyte. In primary oocytes, the nucleus is large and present in the center.
The oocytes are the immature female gametes that mature in an ovary, within a follicle to form the mature female gamete- ova or egg. The process of formation of ova or egg in the females is called Oogenesis. It begins in the early embryonic period in the females, from the 7th week of gestation. The oogonium is formed from the primordial germ cells and increase in number through mitotic cell division. The oogonium grows till the 5th month of the pregnancy, and no new oogonium- is further added. A large number of these cells degenerate till birth. The maturation of these cells occurs to form the- primary and the secondary oocyte. The secondary oocyte splits into two cells in the second meiotic division- an ootid and a polar body. At the time of ovulation, one ootid is released from the follicle, which matures into an ovum when a sperm penetrates it. The fusion of the two gametes results in the formation of a diploid zygote.
The various structures seen in a primary oocyte are-
1)Corona Radiata- It is a layer formed by follicle cells and has a multicellular thickness. It derives itself from the cumulus oophorus cells- and provides vital proteins to the cells. It is present adjacent to the zona pellucida.
2)Zona Pellucida- It is formed by the secretions of oocytes and follicular cells. It is made up of glycoproteins and surrounds the plasma membrane of the oocyte.
3)Follicular cavity- The appearance of a follicular cavity or antrum- in an oocyte indicates the development of a secondary follicle from the primary follicle. This cavity is filled with follicular fluids and provides a microenvironment for the development of the oocyte.
4)Perivitelline space- The space found between the zona pellucida and the cell membrane of an oocyte is called the- perivitelline space.
5)Germinal Vesicle- It is the enlarged nucleus of the egg that contains the chromatin and nucleolus.
Let us analyze the options to find the correct answer.
Arrow A) points towards the- zona pellucida of the oocyte.
Arrow B) points towards the- corona radiata of the oocyte.
Arrow C) points towards the- perivitelline space of the oocyte.
Arrow D) points towards the- germinal vesicle of the oocyte.
Option E): A- Zona pellucida, B- Corona radiata, C- Perivitelline space, D- Germinal Vesicle is the correct option.
All the other options are irrelevant.
Hence, the correct answer is option (E)
Note: The primary oocytes remain arrested in the- Prophase stage of Meiosis I after birth. They resume Meiosis during puberty or sexual maturity. During each menstrual cycle- a set of primary oocytes resumes the process of Meiosis I to develop into a secondary oocyte after the action of various hormones like- FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

What is the stopping potential when the metal with class 12 physics JEE_Main

The momentum of a photon is 2 times 10 16gm cmsec Its class 12 physics JEE_Main

Using the following information to help you answer class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following would not be a valid reason class 11 biology CBSE

Why should electric field lines never cross each other class 12 physics CBSE

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic class 11 biology CBSE

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Write two differences between autotrophic and heterotrophic class 10 biology CBSE

Angle inscribed in a minor segment is A acute B obtuse class 10 maths CBSE

Derive an expression for electric potential at point class 12 physics CBSE

Distinguish between Khadar and Bhangar class 9 social science CBSE

Write down 5 differences between Ntype and Ptype s class 11 physics CBSE