. Elementary botany. Botany. 36o RELA TION TO ENVIKONAfENT. (fig. 417). Surrounding the plerome and tilling the space between it and the dermatogen is the third formative tissue called the periblem, which later forms the cortex (bark or rind), and consists of parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, or cork, etc., as the case may be. It should be understood that all these different forms and kinds of cells have been derived from meristem by gradual change. In the mature stems, therefore, there are three distinct regions, the central cylinder or stele, the corte.x, and the epidermis. 710. Central
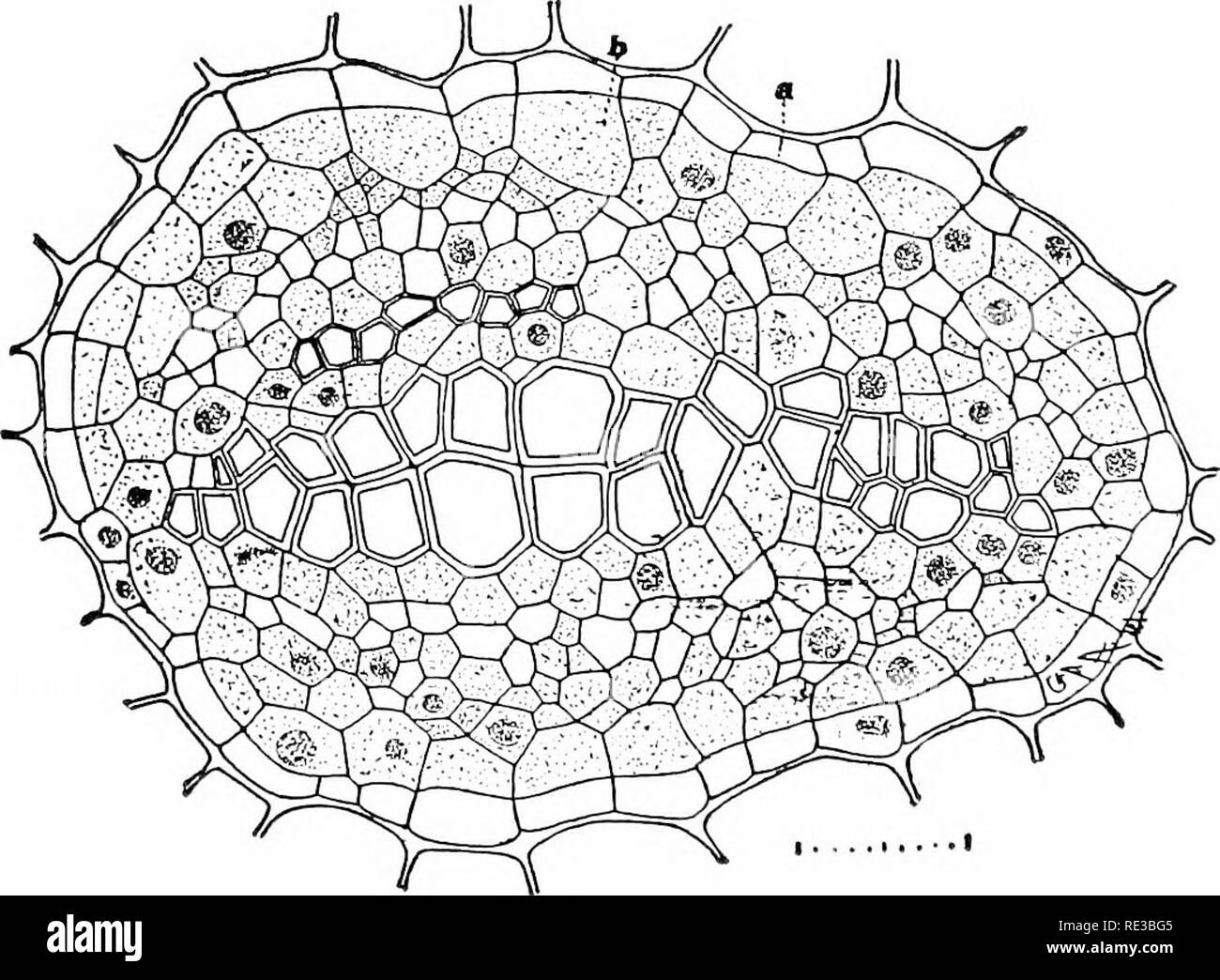
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RE3BG5File size:
7.1 MB (426.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1845 x 1354 px | 31.2 x 22.9 cm | 12.3 x 9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Elementary botany. Botany. 36o RELA TION TO ENVIKONAfENT. (fig. 417). Surrounding the plerome and tilling the space between it and the dermatogen is the third formative tissue called the periblem, which later forms the cortex (bark or rind), and consists of parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, or cork, etc., as the case may be. It should be understood that all these different forms and kinds of cells have been derived from meristem by gradual change. In the mature stems, therefore, there are three distinct regions, the central cylinder or stele, the corte.x, and the epidermis. 710. Central cylinder or stele.—As the central cylinder is organized from the plerome it becomes differentiated into the vascular bundles, the pith, the pith rays (medullary rays) which radiate from the pith in the center between the bundles out to the corte.x, and the pericycle, a layer of cells lying between the central cyUnder and the cortex. The bundles then are farther organized into the x}'lem and phloem portions with their different elements, and the fascicular cambium (meristem) separating the xj'lem and phloem, as described in Chapter V. Such a bundle, where the xylem and phloem portions are separated by the cambium is called an open bun-. Fit;. 418. Concentric bundle frDin stem of Polypodiuni vulgare. Xylem in the center, surrounded by phloem and this b' the endodermis. (From the author's Biology of Fern.s.) die fas in fig. 58). Where the [ihloem and wlciii lie siilc >- side in the same radius the bundle is a ro/ldltval one. 1 >ii(>lle(!ons and coin'fcrs arc char- acterized by open collateral bundles. This is why trees and many other. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Atkinson, George Francis, 1854-1918. New York : H. Holt