. Elementary text-book of zoology. GAD us. 331 and the consequent modification in development is in an intermediate position. The three types will be compared after the frog has been dealt with (see page 358). III.—GADUS. Phylum - Chokdata (p. 402). Sub-Phylum Vertebrata (p. 405). Class Pisces (p. 434). Order Teleostomi (p. 437). The haddock (Gadus csglefinus) is one of the commonest and best known of our British fishes. It is described here as a type of the order Teleostomi or bony fishes. The haddock is a smaller fish than the cod Colour and '^"' '^'^S^'^ ^^^^ ^^^ whiting; all three bel
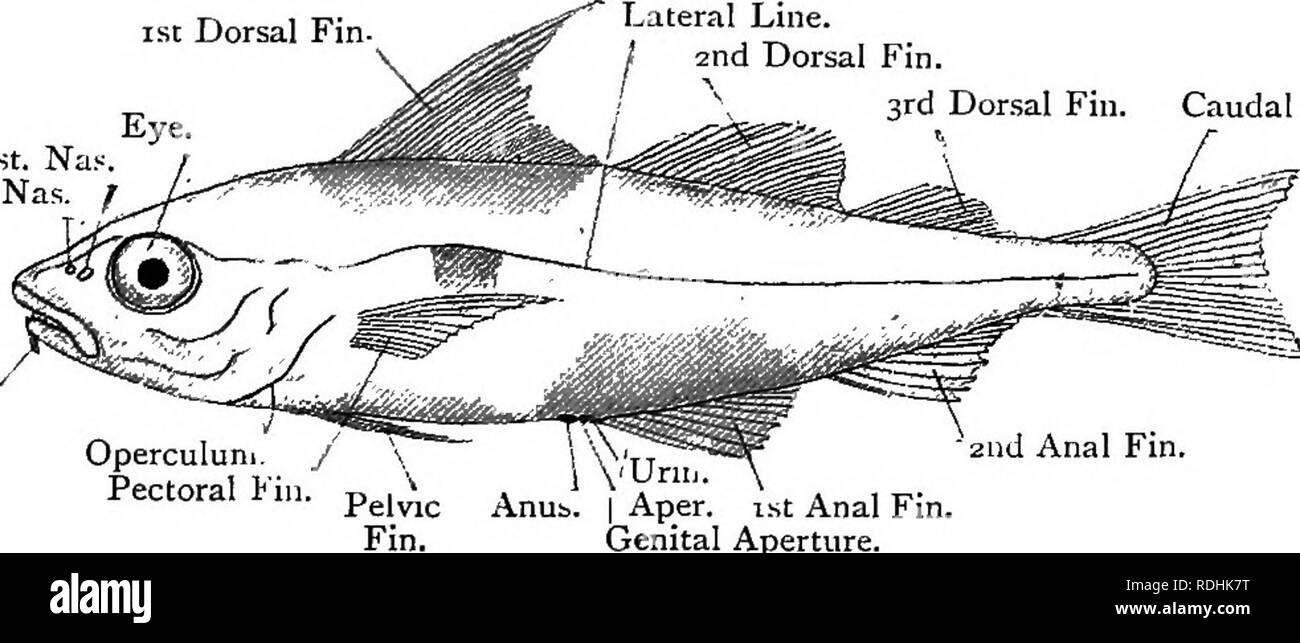
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RDHK7TFile size:
7.1 MB (304 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
2423 x 1031 px | 41 x 17.5 cm | 16.2 x 6.9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Elementary text-book of zoology. GAD us. 331 and the consequent modification in development is in an intermediate position. The three types will be compared after the frog has been dealt with (see page 358). III.—GADUS. Phylum - Chokdata (p. 402). Sub-Phylum Vertebrata (p. 405). Class Pisces (p. 434). Order Teleostomi (p. 437). The haddock (Gadus csglefinus) is one of the commonest and best known of our British fishes. It is described here as a type of the order Teleostomi or bony fishes. The haddock is a smaller fish than the cod Colour and '^"' '^'^S^'^ ^^^^ ^^^ whiting; all three belong to the Habits. '^''S^ family of Gadida. It frequents the deeper offshore water and is a ground-feeder upon small Crustacea, Molhisca and Annelida. The freshly-caught haddock is of a beautiful colour. The ventral surface is a pearly-white which gradates up Fig. 235.—Lateral View of the Haddock {Gadus aglejinus) x y^. (Ad nat.) Post. Na«. Ant. Nas. 1st Dorsal Fin Eye. Lateral Line. I 2nd Dorsal Fin Operculun Pectoral V 3rd Dorsal Fin. Caudal Fin.. 2ud Anal Fin, Anus. I Aper. ist Anal Fin. Genital Aperture. each side into a metallic violet darkest along the dorsal surface. Along each side is a thin black line, the lateral line, extending from the head backwards to the tail. Just below the anterior part of this line there is on each side a black spot of pigment. The eyes are Externa.! silvery and black. The whole body is enclothed in an Features investing coat of delicate overlapping cycloid scales, developed in the dermis and carrying no spines. The skin is extremely slimy, as in the skate. At the anterior end of the head is a large gaping mouth armed with upper and lower rows of teeth. Below the cmn is a small sensitive. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Masterman, Arthur Thomas. Edinbu